
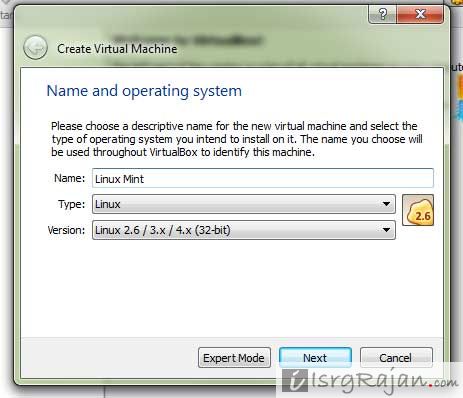
VirtualBox will create the VM and install your chosen flavor of Linux. The default size is 25GB, but I give it more slack since I have lots of space on my drive. VirtualBox reserves this from your existing physical disk space, so ensure you have enough space on your drive. Next, click “Hard Disk” and allocate space for your Linux Virtual Machine. Anything less, and you may encounter problems with some apps later on the VM. The most basic Linux VM can run with surprisingly little memory, but I recommend no less than 2GB. Next, click “Hardware” (see image above) and allocate resources for your Linux VM. Create a New Virtual Machineĭo not click “Finish” until you've allocated system resources to your VM. That will let you mount it as a virtual CD on your VM. Remember that you must download the Linux distribution as an ISO file. If you aren't sure what to get – Ubuntu Desktop, CentOS, Debian are some good Linux builds for beginners. When downloading your Linux distribution, try downloading it from the official website as much as possible. While there are some popular distributions, such as Ubuntu and Debian, you can technically choose from hundreds of others. Part of the beauty of Linux is that so many variants exist. Once you have installed VirtualBox, you must download a Linux distribution. Once the download is complete, run the installation file and follow the on-screen instructions to install VirtualBox on your computer.

Go to the VirtualBox download page and download the latest version for Windows.

VirtualBox is a free and open-source virtualization software from Oracle that enables you to run multiple operating systems on a single computer. The VirtualBox interface is clean and easily navigable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
